NCLEX-PN Practice Test Questions
The NCLEX-PN examination is the National Council Licensure Examination for Licensed Practical Nurses. In the past, a similar examination was referred to as the “State Board” for a nursing license. Passing the NCLEX-PN examination gives your state the authority to grant you a nursing license after the completion of a state approved school for practical nursing.
The content of the NCLEX-PN Test Plan consists of four major sections, each of which test your knowledge, skills and abilities to meet these client needs. These categories, or sections, and the percentage of questions you should expect to see in this examination are:
- Safe and Effective Care Environment
- Coordinated Care (16% to 22%)
- Safety and Infection Control (10% to16%)
- Health Promotion and Maintenance (7% to 13%)
- Psychosocial Integrity (8% to 14%)
- Physiological Integrity
- Basic Care and Comfort (7% to 13%)
- Pharmacological Therapies (11% to 17%)
- Reduction of Risk Potential (10% to 16%)
- Physiological Adaptation (7% to 13%)
In addition to the above categories, the questions will also contain ongoing essential themes and skills such as clinical problem solving using the nursing process, communication, caring/compassion, teaching/learning and documentation.
Lastly, most of the questions are multiple choices questions with four items, only one of which is correct. Others are alternative format questions such as choosing all the items where more than one item is correct, fill in the blanks and listing priorities or steps in a procedure from the first to the last. You will see all types of questions in our practice examination for licensed practical nurses.

Let's get started...
1. Select the member of the healthcare team that is paired with one of the main functions of this team member.
- Occupational therapist: Gait exercises
- Physical therapist: The provision of assistive devices to facilitate the activities of daily living
- Speech and language therapist: The treatment of swallowing disorders
- Case manager: Ordering medications and treatments
Correct Response: C
Speech and language therapists assess and treat patients with a swallowing disorder; they also assess and treat patients with speech and communication problems as often occurs after a cerebrovascular accident, or stroke. Occupational therapists assist patients with their activities of daily living and they also provide patients with assistive devices to facilitate eating and dressing. Physical therapists perform rehabilitation and restorative care including help with ambulation and balance/gait exercises. Lastly, case managers coordinate care along the continuum of care and they manage insurance reimbursements.
2. The recommended daily caloric intake for sedentary older men, active adult women and children is:
- 2400 calories
- 1600 calories
- 2800 calories
- 2000 calories
Correct Response: D
Sedentary older men, active adult women and children should all have 6 ounces of grains, 2½ cups of vegetables, 2 cups of fruits, and 3 cups of milk to help make up their 2000 calorie requirement. Sedentary adolescents require 2400 calories, sedentary women and children require 1600 calories and active adolescents need 2800 calories daily.
3. Ill health, malnutrition, and wasting as a result of chronic disease are all associated with:
- Surgical asepsis
- Catabolism
- Cachexia
- Venous stasis
Correct Response: C
Ill health, malnutrition, and wasting as a result of chronic disease are all associated with cachexia. Cachexia can also result from dehiscence of a surgical incision or rupture of wound closure. Surgical asepsis refers to using a sterile technique to protect against infection before, during, and after surgery. The breakdown of tissue, especially after severe trauma or crush injuries is known as catabolism. Venous stasis is a disorder related to pooling of blood in a vein of the body; venous stasis typically occurs in the lower extremities and it is one of the many hazards, or complications, of immobilization.
4. Select all the possible opportunistic infections that adversely affect HIV/AIDS infected patients.
- Visual losses
- Kaposi’s sarcoma
- Wilms’ sarcoma
- Tuberculosis
- Peripheral neuropathy
- Toxoplasma gondii
Correct Response: B, D, F
Kaposi’s sarcoma, tuberculosis, toxoplasma gondii, mycobacterium avium, herpes simplex, histoplasmosis and salmonella infections are HIV/AIDS associated opportunistic infections. Although many affected patients can experience blindness and peripheral neuropathy, these disorders result from impaired nervous system damage rather than an infection. Lastly, Wilms’ tumor is a pediatric form of kidney cancer and it is neither an infection nor something that typically affects the patient with HIV/AIDS.
5. What can help reduce a patient’s anxiety and postsurgical pain?
- Preoperative teaching
- Preoperative checklist
- Psychological counseling
- Preoperative medication
Correct Response: A
Patient teaching before surgery not only helps to reduce a patient’s anxiety and postsurgical pain but it also decreases the amount of anesthesia needed and a lack of anxiety additionally speeds up wound healing. Preoperative checklists are a form of nursing documentation that is used to guide and document the care of the patient before surgery. Psychological counseling is typically NOT necessary except under highly unusual circumstances and preoperative medication can decrease the amount of anesthetic needed and respiratory tract secretions but it does not help with postoperative pain.
6. Which disease decreases the metabolic rate?
- Cancer
- Hypothyroidism
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Cardiac failure
Correct Response: B
Hypothyroidism causes a decreased metabolic demand, so fewer calories are required. Cancer, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or cardiac failure all increase the metabolic demands and the need for added calories.
7. When caring for an infant during cardiac arrest, which pulse must be palpated to determine cardiac function?
- Carotid
- Brachial
- Pedal
- Radial
Correct Response: B
The brachial pulse is the most accessible pulse on an infant and, therefore, it is the site of choice. The carotid pulse may be difficult to palpate due to the fatty tissue that typically, and often, surrounds an infant’s neck. Lastly, the radial and pedal pulses may not be reliable indicators of cardiac function.
8. The patient should be sitting when deep breathing and coughing because this position:
- Is physically more comfortable for the patient
- Helps the patient to support their incision with a pillow
- Loosens respiratory secretions
- Allows the patient to observe their area and relax
Correct Response: B
The patient should be sitting when deep breathing and coughing because this position allows the patient to be better able to splint the incision with a pillow which provides abdominal support during coughing. It also allows the lungs to more fully expand because the diaphragm drops. The most comfortable position for the patient is the supine position; however, this position does not permit the lungs to fully expand. There is no association or correlation between loosening respiratory secretions or relaxation with this sitting position.
9. Which procedures necessitate the use of surgical asepsis techniques? Select all that apply.
- Intramuscular medication administration
- Central line intravenous medication administration
- Donning gloves in the operating room
- Neonatal bathing
- Foley catheter insertion
- Emptying a urinary drainage bag
Correct Response: B,C,E
Surgical asepsis is used when managing central line intravenous medication administration, when donning sterile gloves in the operating room and when inserting an indwelling Foley catheter. Medical asepsis, or clean technique, is used when bathing a neonate, when emptying a urinary drainage bag and when administering an intramuscular medication injection.
10. What is the ultimate purpose and goal of performance improvement activities?
- To increase efficiency
- To contain costs
- To improve processes
- To improve policies
Correct Response: C
The ultimate purpose of quality improvement activities is to identify process flaws and then to change the process so that it is fail proof. Fail proof processes prevent human error and possible patient harm. Although these process improvements and changes may also increase efficiency and decrease costs, the ultimate goal of quality improvement activities is to prevent future occurrences with process changes and not costs and efficiency. Lastly, it is known that processes, not policies, are the root cause of many medical errors.
11. The primary difference between practical nursing licensure and a nursing certification in an area of practice is that nursing licensure is:
- Insures competency and a nursing certification validates years of experience.
- Mandated by the American Nurses Association and a nursing certification are not.
- Is legally mandated by the states and a nursing certification is not.
- Renewed every two years and a nursing certification is renewed every five years.
Correct Response: C
The primary difference between practical nursing licensure and a nursing certification in an area of practice is that nursing licensure is legally mandated by the states and NOT the American Nurses Association and a nursing certification is not mandated. To practice nursing without a current and valid license is contrary to the law. Nursing licenses are renewed every two years and nursing certifications are typically renewed every three years, however, this may vary according to the particular certification. Passing the NCLEX examination and receiving a nursing license indicates that the graduate has at least the minimal competency necessary to provide safe patient care. Nursing certifications, on the other hand, validate expertise in a particular area of nursing practice.
12. What intervention is the best to relieve constipation during pregnancy?
- Increasing the consumption of fruits and vegetables
- Taking a mild over-the-counter laxative
- Lying flat on back when sleeping
- Reduction of iron intake by half or more
Correct Response: A
Dietary roughage (or fiber) with sufficient fluids and exercise may help relieve constipation. Over-the-counter medications should be avoided during pregnancy. The supine position can place additional pressure on the aorta and vena cava, leading to vena cava syndrome. A reduction of iron supplements during pregnancy may reduce hemoglobin production and result in a less than an effective immune system.
13. You are the LPN working on 2 east with adult medical surgical patients. Your unit has been instructed to perform a horizontal evacuation of your patients because there is a fire on 1 east. Where will you evacuate your patients to?
- 3 west
- 3 east
- 2 west
- 1 west
Correct Response: C
You would evacuate your patients to west. A horizontal evacuation is the movement of patients to another area of the same floor. A vertical evacuation is the movement of patients to a different floor or level of the building. Patient evacuations are done to prevent patient injury. Under no circumstances should the elevators be used for evacuations.
14. Which electrolyte is essential for enzyme and neurochemical activities?
- Chloride
- Magnesium
- Potassium
- Phosphate
Correct Response: B
Magnesium is essential for enzyme and neurochemical activities and it is also needed for cardiac and skeletal muscle excitability. Chloride is the most abundant negatively charged ion in extracellular fluid with potassium being the most abundant positively charge ion. Phosphate assists in acid-base regulation.
15. Number the choices below to reflect the correct sequence for using a fire extinguisher:
- Aim at the base of the fire
- Squeeze the handle
- Sweep back and forth
- Pull the pin
Correct Response: D, A, B, C
The correct sequence of action for using a fire extinguished is easily remembered by keeping the PASS acronym in mind. P is pulling out the pin to activate the fire extinguisher; A is to aim the fire extinguisher at the base of the fire; S is to squeeze the handle to discharge the contents of the fire extinguisher; and S is sweep back and forth over the base of the fire while discharging the contents.
16. As you are working you suspect that another licensed practical nurse is verbally and physically abusing a patient. What is the first thing that you will do?
- Nothing because you are not certain that it is occurring
- Nothing because you only suspect the abuse
- Call the police or the security department
- Report your suspicions to the charge nurse
Correct Response: D
Nurses and other healthcare providers are mandated by law to report all suspected abuse and neglect. You do NOT have to be certain about it; an expert will perform the investigation. You do not contact the police or the security department; the charge nurse will follow established procedures for notifications not the licensed practical nurse.
17. Which of the following is the World Health Organization’s (WHO) definition of health?
- The absence of all illness and disease
- The absence of any comorbidities
- A holistic state of wellbeing
- A use of health promotion activities
Correct Response: C
The World Health Organization (WHO) defines health as a holistic (wholistic) state of wellbeing. This state of wellbeing is far more than the absence of illness, diseases and comorbidities. Lastly, the use of health promotion activities does promote health but these activities do not define health according to the World Health Organization.
18. Which nursing theorist believes that most patients are capable of performing self care?
- Dorothea Orem
- Madeleine Leininger
- Martha Rogers
- Sister Callista Roy
Correct Response: A
Dorothea Orem developed the Self Care theory or model. This theory maintains that some patients are completely compensatory and totally dependent on the nurse for care, other patients are partially compensatory and need only assistance by the nurse and others are totally independent in terms of their self care needs. Madeleine Leininger developed the Transcultural Nursing theory; Martha Rogers developed the Science of Unitary Human Beings theory and Sister Callista Roy developed the Adaptation theory of nursing practice.
19. What element is minimally assessed during a basic prenatal physical examination?
- Palpation and auscultation of the abdomen
- Examination of the anus and rectum
- Urinalysis for glucose, protein and ketones
- Visual assessment of cervix and vagina
Correct Response: C
A urinalysis is considered routine during the prenatal examination. Assessment of the cervix, vagina, anus, rectum, and palpation and auscultation of the abdomen may not be checked until a complete gynecologic examination is done by the doctor.
20. A positive over-the-counter pregnancy test is considered a:
- Possible sign of pregnancy.
- Presumptive sign of pregnancy.
- Probable sign of pregnancy.
- Positive sign of pregnancy.
Correct Response: C
A positive pregnancy test and changes in the reproductive organs are both considered probable signs of pregnancy. Presumptive signs include amenorrhea, frequent urination and pigment changes in skin. Determining the estimated day of birth or delivery (EDB or EDD) is considered to be a positive sign of pregnancy.
21. Select all of the signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism.
- Cool skin
- Thickened bodily hair
- Heat intolerance
- Constipation
- Insomnia
- Increased appetite
- Palpitations
Correct Response: C,E,F,G
The signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism include heat intolerance, increased appetite, palpitations and insomnia among others such as thinning hair, the loss of hair, increased sweating, weight loss, emotional instability and diarrhea.
22. During which phase of the nursing process does data get collected and validated with the patient and/or family members by the nurse?
- The implementation phase
- The assessment phase
- The evaluation phase
- The planning phase
Correct Response: B
Subjective, objective, primary and secondary data is collected and validated with the patient and/or family members by the nurse during the assessment phase of the nursing process. The implementation phase is the actual care of the patient; the evaluation phase includes the comparison of current data to expected outcomes to determine if the patient has achieved the pre-established goals and the planning phase consists of priority setting and care planning.
23. Which of the following is the best worded expected outcome?
- “The nurse will provide for adequate hydration”
- “The nurse will insure that the patient is safe”
- “The patient will cough and deep breathe every two hours”
- “The patient will value health”
Correct Response: C
“The patient will cough and deep breathe every two hours” is the best worded expected patient outcome. This outcome or goal is specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, within a specified timeframe, trackable and it should be agreed to by the patient. All expected outcomes are worded in terms of what the patient, not the nurse, will do and it should also be specific and measurable. “The patient will value health” is not measurable.
24. What is a major difference between a problem oriented medical record and a source oriented medical record?
- The problem oriented medical system has a centralized part of the chart for interdisciplinary progress notes and the source oriented medical record has separate areas for each profession’s progress notes.
- The problem oriented medical system consists of narrative progress notes and the source oriented medical record uses SOAP.
- The source oriented medical system uses charting by exception and the source oriented medical record system does not.
- The source oriented medical system has a centralized part of the chart for interdisciplinary progress notes and the problem oriented medical record has separate areas for each profession’s progress notes.
Correct Response: A
The problem oriented medical system has a centralized part of the chart for interdisciplinary SOAP progress notes and the source oriented medical record has separate areas for each profession’s progress notes. Although source oriented medical records can use SOAP, this is not a defining characteristic and most of these notes are free formed narrative notes. Charting by exception is a distinctly different medical system than source or problem oriented medical systems.
25. Which of the following are necessary elements of malpractice? Select all that apply.
- A breach of duty
- An intentional act
- A nonintentional act
- Forseeability
- Patient harm
- Causation
Correct Response: A,D,E,F
The necessary elements of malpractice are a duty to the patient, a breach of duty, foreseeability, causation, and patient harm. The breach of duty can be intentional or nonintentional.
26. Select the following fire emergency interventions in correct sequential order.
- Pull the fire alarm.
- Contain the fire.
- Rescue patients in danger.
- Extinguish the fire.
Correct Response: C,A,B,D
The RACE acronym is used to prioritize and sequence the steps that must be followed when a fire occurs. R stands for rescue patients; A is pulling the fire alarm; C is to contain the fire by closing doors, etc.; and E is extinguishing the fire with a fire extinguisher when possible.
27. After your patient has been told that they have Cushing’s syndrome, the patient asks you what Cushing’s syndrome is. How would you respond to this patient’s question?
- “Cushing’s syndrome is a type of irritable bowel syndrome.”
- “Cushing’s syndrome is a disorder of the adrenal gland.”
- “Cushing’s syndrome often occurs among patients who are getting radiation therapy.”
- “Cushing’s syndrome often occurs among patients who are chemotherapy.”
Correct Response: B
Cushing’s syndrome is a disorder of the adrenal gland. It results from the chronic hypersecretion of glucocorticoids from the adrenal cortex. It is Crohn’s disease, not Cushing’s syndrome, that is a type of irritable bowel syndrome and, there is no relationship between Cushing’s syndrome and radiation or chemotherapy.
28. You are preparing a sterile field for a operating room surgical procedure. When should you stop the preparation of this sterile field?
- When you have placed a sterile item only 1 inch and not 2 inches from the edge of the sterile field
- When you have completely finished the field. You cannot stop the set up until it is all done.
- When you have accidentally poured a sterile liquid into a container that was on the sterile field
- When you turn your upper body only away from the field because the surgeon calls your name
Correct Response: D
You must stop the preparation of the sterile field and begin all over again when you have turned your upper body away from the field because sterile technique has been violated and the sterility of the field has been broken even when on turns away from the sterile field even for a second. Sterile items must be placed within one inch, not two inches from the edge of the sterile field. Lastly, sterile solutions can be poured into sterile containers on the sterile field without breaking the techniques required according to surgical asepsis.
29. Avulsed teeth should be placed in:
- Normal saline.
- Cold water.
- Milk.
- Warm water.
Correct Response: C
Avulsed teeth should be immediately placed in milk. An avulsed tooth is the traumatic loss of a tooth. In addition to placing the tooth in milk, the tooth should only be handled at the crown and not the root of the tooth. These interventions preserve the tooth for reimplantation.
30. You are working in a pediatric unit of the hospital and caring for a six year old boy who is hospitalized with cystic fibrosis and respiratory compromise. Which developmental task is the challenge for this boy at his age?
- To cough, deep breathe and improve respiratory status
- To establish industry and self confidence
- To develop autonomy and self control
- To develop initiative and a sense of purpose
Correct Response: D
According to Erik Erikson, a developmental psychologist, the preschool child is challenged with initiative, the development of confidence and a sense of purpose. The other age groups along the life span and their developmental tasks are listed below:
Infant: Trust
Toddler: Autonomy, self control and will power
School Age Child: Industry, self-confidence and competency
Adolescent: Identity formation and a sense of self
Young Adult: Intimacy, affection and love
Middle Aged Adult: Generativity, productivity and concern about others
Older Adults: Ego integrity, wisdom and satisfaction with life
31. The embryonic period during pregnancy takes place from:
- Weeks 1 to 12.
- Weeks 1 to 10.
- Weeks 3 to 5.
- Weeks 6 to 10.
Correct Response: D
The embryonic period begins around week 6, following the ovulation period of weeks 1 to 2 and the cell division and implantation period from weeks 3 to 5. The first trimester runs from week 1 until week 12.
32. Place these human needs in order from the greatest priority to the least priority using # 1 as the greatest priority and # 5 as the least of all in terms of priority.
- Self esteem and esteem by others
- Self actualization
- Psychological needs
- Love and belonging
- Physiological needs
Correct Response: E,C,D,A,B
According to Abraham Maslow, the hierarchy of human needs from the most basic and necessary to the least priority are the physiological or biological needs, the safety and psychological needs, the need for love and belonging, self esteem and the esteem by others and self actualization. Maslow’s theory states that until the most basic priority needs are satisfied in a step wise manner, the less priority needs cannot be addressed and fulfilled.
33. During which week does the fetal heart begin pumping its own blood?
- 3rd week
- 5th week
- 9th week
- 6th week
Correct Response: A
The embryonic heart begins pumping its own blood, often a different blood type than the mother’s, during week 3. Week 5 includes the development of eyes, legs, and hands. Brain waves become detectable during week 6 and teeth begin to develop during week 9 of gestation.
34. Which of the following is a vector of infection?
- A contaminated ball
- A contaminated thermometer
- An infected person
- An infectious fly
Correct Response: D
An infectious fly is an example of a vector that can transmit infection. Other vectors, or nonhuman living beings that can transmit infections to humans, include mice, vermin and mosquitoes. Inanimate items that can spread infection by contact are referred to as fomites. Examples of fomites include a contaminated thermometer, balls and door knobs. An infected human being is a host according to the chain of infection and not a vector.
35. Which oral disorder appears as yellow or white spots on the oral mucosa that are not possible to scrape off without bleeding?
- Herpes simplex
- Candidiasis
- Alphthous ulcers
- Leukoplakia
Correct Response: B
Oral candidiasis is characterized with yellow or white spots on the oral mucosa that are not possible to scrape off without bleeding, therefore, no attempts to remove these spots should be done. Herpes simplex is marked with tingling and burning of the lips and mouth areas as well as blisters and a sore throat. Alphthous ulcers, or canker sores, are sore oral lesions; and oral leukoplakia leads to thickened, white patches on the cheeks, tongue, lower lip, or on the floor of the mouth.
36. Which type of cancer has the poorest prognosis?
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- Breast cancer
- Pancreatic cancer
- Gastric cancer
Correct Response: C
Of all of the above types of cancer, it is pancreatic cancer that has the poorest prognosis. This is based on the fact that pancreatic cancer is not symptomatic, and therefore, it is diagnosed after the point when a surgical removal can be performed. It has a rapid course and it is characterized with a high degree of mortality.
37. States throughout our nation vary somewhat in terms of things that nursing assistants can and cannot legally do. Which statements about these state to state differences are accurate? Select all that apply.
- Nursing assistants can change catheter tubings but not catheters
- Nursing assistants can change sterile dressings
- Nursing assistants have an expanding role in many states.
- Nursing assistants cannot assess the physical status of the patients.
- Nursing assistants can apply topical medication lotions to intact skin.
- The trend is moving toward nurses only staffing patterns.
Correct Response: C,D
Nursing assistants have an expanding role in many states. For example, some states permit nursing assistants to take ECGs, or EKGs, and to perform phlebotomy when they are given the necessary training and have been deemed competent to do so. Only nurses assess; nursing assistants cannot assess the physical status of the patients.
Nursing assistants cannot perform any sterile procedures. For example, they cannot change catheter tubings and they cannot change sterile dressings. Lastly, nursing assistants do not administer medications. Topical skin lotions that contain a medication is considered a medication, therefore, the nursing assistant cannot apply them.
38. A cesarean mode of delivery, often utilized for various reasons, is the most common mode for females with which pelvic type?
- Android
- Anthropoid
- Gynecoid
- Platypelloid
Correct Response: A
Android pelvic types are heart shaped and found among 23% of all women. Gynecoids are round pelvic types and the most common type at about 50%. Oval shaped pelvic types are anthropoid and found at a rate of 24%. Platypelloids are flat and the least common pelvic type at 3%.
39. How many bones make up a newborn’s skull?
- 8
- 4
- 6
- 5
Correct Response: D
The typical newborns skull will consist of two frontal bones, two parietal bones, and an occipital bone for 5 total bones. Sutures divide these bones and there are 6 fontanelles, or soft spots, where the sutures intersect one another.
40. Your patient has just returned from the diagnostic imaging department and the doctor has told the patient that they have a Mallory-Weiss tear. The patient asks you what a Mallory-Weiss tear is. How should you respond to this patient?
- “A Mallory-Weiss tear is a kind of diverticulitis.”
- “A Mallory-Weiss tear is an esophageal tear”
- “A Mallory-Weiss tear is a lacrimal gland disorder.”
- “A Mallory-Weiss tear is a tear that results from a peptic ulcer.”
Correct Response: B
A Mallory-Weiss tear is an linear tear of the esophageal mucosa. Alcohol use and abuse are the most commonly occurring risk factors. These tears are not associated with peptic ulcers or diverticulitis. The lacrimal glands in the eyes produce tears to lubricate the eyes.
41. You have been asked to speak at a new nursing assistants' orientation class about infection control and handwashing techniques. What would you include in this teaching?
- Demonstrate the correct one minute handwashing procedure using soap and running water.
- Demonstrate the correct 2 minute handwashing procedure using soap and running water.
- Using hot water so that the natural fats on the skins are emulsified with the soap.
- Using cold water so that the natural fats on the skins are emulsified with the soap.
Correct Response: B
The best way to teach the techniques of handwashing is to actually demonstrate the correct handwashing procedure. Proper handwashing must be done for a minimum of two minutes. Warm not cold water or hot water is used for handwashing.
42. How many minims are contained in 1 milliliter?
- Between 10-11
- 12
- 20
- Between 15 or 16
Correct Response: D
A minim is 1⁄480 of a fluid ounce or .0020833333333333 oz. 1 milliliter equals .033814 ounces.
43. Periwound maceration occurs when:
- The skin around the wound softens and is damaged.
- Selecting a dressing individualized to the type of wound.
- Negative-pressure to “air out” the wound is used.
- The skin around the wound dries out and hardens.
Correct Response: A
Periwound maceration, also classified as moisture associated skin damage, is the softening of the skin and damaging of connective fibers which leads to the wound drying out and hardening. Dressing selection can help prevent this complication, and negative pressure may reduce it by reducing edema.
44. Which patient is at greatest risk for cholelithiasis and choledocholithiasis?
- A 70 year old male patient who has liver disease
- A 70 year old female patient who has liver disease
- A 50 year old male patient who is Asian
- A 50 year old female patient who is Asian
Correct Response: B
The 70 year old female patient who has liver disease is at the greatest risk because the female gender, advancing age and the liver disease are known risk factors for cholelithiasis and choledocholithiasis. Other risk factors include obesity, oral contraceptive use, diseases and disorders of the ileum, hypercholesterolemia and races like the Hispanic, Native American and Caucasian races.
45. Select the method of special precautions that is accurately paired with the personal protective equipment that is minimally required in order to prevent the spread of infection.
- Contact precautions: Gowns, gloves and mask
- Droplet precautions: Face mask
- Airborne transmission precautions: Negative pressure room
- Contact precautions: Gloves
Correct Response: B
The minimal personal protective equipment that is required for droplet precautions is a face mask. Contact precautions minimally require the use of gloves and gowns; and airborne transmission precautions minimally require the use of a negative pressure room, a HEPA mask, gowns and gloves.
46. Which statement about Meniere’s disease is accurate and true?
- Meniere’s disease most commonly occurs among members of the elderly population.
- Meniere’s disease is insidious and it always affects both ears.
- Meniere’s disease occurs with an impairment of the second cranial nerve.
- Antiemetic drugs are used for the treatment of patients affected with Meniere’s disease.
Correct Response: D
Antiemetic drugs as well as other drugs to treat the vertigo, like Antivert, as well as diuretics are used for the treatment of patients affected with Meniere’s disease. Meniere’s disease typically affects only one ear; it is not the result of second cranial nerve damage. Lastly, people in their 40s and 50s are at greater risk for Meniere’s disease and not the elderly.
47. Which of these patients is affected with a healthcare acquired infection?
- A 18 year old male patient who developed a intravenous line infection two days after insertion
- A 72 year old male patient who is at risk for infection secondary to AIDS/HIV
- A 67 year old female patient who was admitted with a urinary tract infection
- A 5 year old pediatric patient who develops the measles rash 3 days after admission
Correct Response: A
The 18 year old male patient who developed a intravenous line infection two days after insertion is affected with a healthcare related, or nosocomial, infection. These infections include all infections that occur while the patient is receiving healthcare services. The patient who was admitted with a urinary tract infection and the pediatric patient who develops the measles rash 3 days after admission acquired these infections prior to receiving healthcare services so they are not considered healthcare related, or nosocomial, infections. Lastly, the 72 year old male patient who is at risk for infection secondary to AIDS/HIV has not yet been infected; he is simply at risk for infection.
48. The stages of infection in correct sequential order are:
- The prodromal, incubation, illness and convalescence stages
- The incubation, prodromal, illness and convalescence stages
- The prodromal, primary, secondary and tertiary stages
- The inflammation, infection and immunity stages
Correct Response: B
The incubation, prodromal, illness and convalescence stages are the stages of infection in correct sequential order. Inflammation, infection and immunity are commonly used terms in infection control but they are not stages of the infection process. Primary, secondary and tertiary are levels of prevention and not stages of the infection process.
49. What is the single most important thing that nurses do in order to prevent the spread of infection?
- Applying standard precautions
- Using personal protective equipment
- Adhering to the principles of asepsis
- Handwashing
Correct Response:
Handwashing is the single, most important thing that nurses, and other healthcare professionals, can do in order to prevent the spread of infection. Applying standard precautions, using personal protective equipment, as indicated, and adhering to the principles of asepsis also prevent the spread of infections; however, handwashing is the single most important thing to prevent the spread of infection.
50. Rh negative maternal blood indicates:
- An incompatibility in the blood between the mother and fetus.
- That antibodies in the mother’s blood are attacking her baby’s blood.
- The mother will require a blood transfusion at the time of delivery.
- The mother does not have a specific marker on her red blood cells.
Correct Response: D
The mother’s red blood cells lacking a specific marker indicate that she is Rh negative. However, incompatibility only occurs if the baby is Rh positive and the mother is Rh negative. This is typically not a problem with a first pregnancy, but in a subsequent pregnancy, the incompatibility can cause the antibodies created during the first pregnancy to attack the new fetus’ red blood cells. A blood transfusion would have no effect on this problem.
51. Low birth weight is defined as a newborn’s weight of:
- 2500 grams or less at birth, regardless of gestational age.
- 1500 grams or less at birth, regardless of gestational age.
- 2500 grams or less at birth, according to gestational age.
- 1500 grams or less at birth, according to gestational age.
Correct Response: A
Low birth weight (LBW) is considered to be a birth weight of less than 2,500 grams regardless of gestational age. Very low birth weight (VLBW) is less than 1500 grams and extremely low birth weight (ELBW) which is less than 1000 grams. Normal weight for a full term neonate is 2500-4200 grams.
52. You are caring for a neonate who has a cleft palate. You should inform the mother that surgical correction will be done when the infant is:
- 8 to 12 months of age.
- 20 to 24 months of age.
- 16 to 20 months of age.
- 12 to 16 months of age.
Correct Response: A
Repairs of cleft palates are typically done before 12 months because this allows for palatal changes associated with normal growth to occur. While repairs can still be performed after one year of age but this increases the likelihood of needing longer-termed treatments and increased risks for poor language development and facial appearance.
53. What percentage of term newborns has a congenital heart disease due to environmental risk factors such as maternal alcoholism or drug ingestion?
- 2% to 4%
- 10% to 20%
- 5% to 10%
- 7% to 9%
Correct Response: C
It is estimated that 5% to 10% of term newborns are born with a congenital heart disease due to environmental risk factors such as maternal alcoholism or drug ingestion. This rate is higher in infants born prematurely. Other environmental risk factors include intrauterine rubella exposure, diabetes mellitus and advanced maternal age in addition to genetic factors.
54. Who should document care?
- The LPNs should document the care that they provided and the care that was given by unlicensed assistive staff.
- The registered nurse must document all of the care that is provided by the nursing assistants because they are accountable for all care.
- All staff members should document all of the care that they have provided.
- All staff should document all of the care that they have provided but the registered nurse, as the only independent practitioner, signs it.
Correct Response: C
All staff members, including unlicensed assistive staff like nursing assistants, document and sign, all of the care that they have personally provided. For example, the nursing assistants will document the vital signs that they have taken; the licensed practical nurses will document all of the treatments and medications that they have given to the patient; and the registered nurse will document nursing diagnoses and assessments that they have completed.
55. Your 54 year old male HIV positive patient has just expired. How should you care for this deceased patient?
- Bathe the patient but it is no longer necessary to use standard precautions because the patient is deceased.
- Place the patient in an negative pressure isolated area of the morgue.
- Double shroud the patient to prevent the spread of infection.
- Bathe the patient using the same standard precautions you used when he was alive.
Correct Response: D
You should bathe your patient as part of post mortem care using the same standard precautions that you did when the patient was alive. The patient is still infectious. Similarly, all patients are bathed after death using standard precautions. Double shrouding and an isolation area in the morgue with negative air pressure are not necessary.
56. Select the types of pain that are accurately coupled with an example of it. Select all that are correct.
- Radicular pain: A broken bone
- Central neuropathic pain: A spinal cord injury
- Peripheral neuropathic pain: A fractured leg bone
- Chronic pain: A stab wound to the chest
- Nocicetive pain: A laceration
- Radicular pain: A herniated spinal disc
Correct Response: B,E,F
A spinal cord injury is an example of an injury that leads to central neuropathic pain; the central nervous system is comprised of the brain and the spinal cord. Lacerations and broken, fractured bones are examples of nociecetive pain and a herniated spinal disc can lead to radicular pain. Stab wound can result in acute, not chronic, pain; and peripheral neuropathic pain can result from carpal tunnel syndrome and post amputation phantom pain.
57. Select the stage of viral hepatitis that is accurately paired with its characteristic(s).
- The prodromal stage: Jaundice begins
- The icteric stage: Flu like symptoms occur
- The preicteric stage: Elevated urine bilirubin levels
- The posticteric stage: Jaundice and dark urine occurs
Correct Response: C
During the preicteric stage of viral hepatitis, elevated urine bilirubin levels, nausea, chills, anorexia, fever and mild upper right quadrant pain occur. The icteric stage is marked with pruritis, clay stools, darkened urine and jaundice. The posticteric stage occurs when the patient returns to near normal physical status. There is no prodromal stage of viral hepatitis.
58. Which nursing diagnosis is the most commonly used among patients who are affected with fibromyalgia?
- Decreased self care in the activities of daily living related to fatigue
- Impaired mental functioning related to electrolyte imbalances
- Increased vigilance secondary to electrolyte imbalances
- At risk for a swallowing disorder related to fibromyalgia
Correct Response: A
The signs and symptoms of fibromyalgia include widespread aching, muscle stiffness, fatigue and sleep disorders. The degree of fatigue can be so severe that the patient is unable to even perform the activities of daily living. Fibromyalgia, a chronic disorder associated with periods of exacerbation and remission is not associated with a swallowing disorder, hypervigilance, mental functioning alterations or electrolyte imbalances.
59. Alcohol, caffeine, or drugs are high risk factors that all fall under which broad classification of risk factors?
- Social demographic
- Environmental
- Biophysical
- Psychosocial
Correct Response: D
Psychosocial risk factors include life style choices like the use or abuse of alcohol, caffeine and illicit drugs in addition to smoking and psychological status. Low income, age, and ethnicity are socialdemographic risk factors. Second hand smoke and air pollution are environmental risk factors; and biophysical risk factors include genetic considerations, nutritional status and disorders such as diabetes.
60. Multifetal pregnancies with triplets occur at a rate of 1 in 8,100 births, but twins occur much more frequently with a rate of:
- 1 in 85 births.
- 1 in 5400 births.
- 1 in 2700 births.
- 1 in 540 births.
Correct Response: A
Twins, whether monozygotic or dizygotic, occur at the rate of about 1 in every 85 births. This rate has seen increases due to various reasons, such as the frequency of fertility treatments and women waiting until later in life to have children; older women, defined as over 35 years old, are more likely to carry multiples than younger women.
61. When a woman has miscarried in three or more consecutive pregnancies, it is referred to as which type of spontaneous abortion?
- Inevitable
- Missed
- Habitual
- Habitual
Correct Response: C
When a woman has miscarried in three or more consecutive pregnancies, it is referred to as habitual abortions. Habitual abortions are often the result of the additional emotional trauma experienced from multiple miscarries. Inevitable abortions are characterizes with bleeding and dilation of the cervical os. When the fetus dies and growth ends, but remains in utero, it is called a missed abortion. Foul-smelling bleeding, fever, and cramping often occur with a septic abortion which is often the result of severe infections.
62. Your long term care patient has chronic pain and at this point in time the patient needs increasing dosages to adequately control this pain. What is this patient most likely to be affected with?
- Drug addiction
- Drug interactions
- Drug side effects
- Drug tolerance
Correct Response: D
Patients with chronic pain are often affected with drug tolerance. Drug tolerance occurs when the patient needs increasing dosages of analgesic medications to adequately control their pain in order to produce the same effect that was produced when the drug was originally begun. Drug addiction, on the other hand, is a constant and compulsive need for a drug even when the use of the drug causes harm to the person. Addiction can occur with or without physical dependence. The need for increasing dosages is not the result of medication side effects or food/drug or drug/drug interactions.
63. The normal sodium level in the body is:
- 135 to 145 milliequivalents.
- 3 to 5 milliequivalents.
- 135 to 145 microequivalents.
- 3 to 5 microequivalents.
Correct Response: A
The normal sodium level in the body is from 135 to 145 milliequivalents, not from 135 to 145 microequivalents.
64. Which type of practice is most similar to research based practice?
- Best practices
- Evidence based practice
- Benchmark practices
- Standard based practice
Correct Response: B
Evidence-based practice is an approach to patient care that encourages nurses to use the best available evidence, or research, in combination with the individual patient’s circumstances and preferences in clinical practice. Simply stated, evidence based practice is research based practice. Best practices may or may not be based on sound research; benchmarks are similar to best practices and these benchmarks are used so that nurses can compare their outcomes of care to those of others. Standards of care are guidelines for practice; standards of care and standards of practice are published by the American Nurses Association as well as other professional organizations and associations.
65. Select the ethical principles that are paired with their description. Select all that apply.
- Justice: Being honest and fair
- Beneficence: Do no harm
- Veracity: Treating all patients equally
- Self determination: Facilitating patient choices
- Beneficence: Do good
- Nonmaleficence: Do no harm
- Self determination: Accountability
Correct Response: D,E,G
The principle of justice requires us to be fair and just to all. Fidelity is being faithful to one’s promises. By the very nature of the implicit nurse-client relationship, the nurse must be faithful and true to their professional promises and responsibilities by providing high quality, safe care in a competent, scientifically grounded manner while upholding the clients’ choices, desires and innate rights. Beneficence means doing good, it is more than not doing harm. Nonmaleficence is “Do not harm”, as stated in the historical Hippocratic Oath. Patient self determination and autonomy is the ethical principle that supports the patient’s right to make their own choices without coercion or the undue influence of others. Lastly, veracity is truthfulness and being honest with the patients.
66. You are caring for a patient with multiple-trauma. Of all of these injuries and conditions, it the most serious?
- A deviated trachea
- Gross deformity of a lower extremity
- Hematuria
- Decreased bowel sounds
Correct Response: A
A deviated trachea is a serious life threatening condition. A deviated trachea is a symptom of tension pneumothorax which can be life threatening. All of the other symptoms will need to be addressed and treated, however, it is the deviated trachea that is the most severe and of the greatest priority.
67. Which statement about appendicitis is accurate and true?
- Appendicitis is more common among females than males.
- A high fiber diet is a risk factor associated with appendicitis.
- Left lower quadrant pain is suggestive of appendicitis.
- Mc Burney’s point tenderness is suggestive of appendicitis.
Correct Response: D
Mc Burney’s point tenderness in the right lower quadrant is suggestive of appendicitis. Appendicitis is more common among males than females and those with a high carbohydrate and/or low fiber diet are at risk for this inflammation and infection.
68. Which skin disorder most closely resembles and mimics dandruff?
- Lice infestation
- Scabies
- Dematitis
- Acne vulgaris
Correct Response: A
Lice infestation with nits most closely resembles and mimics dandruff. Other signs and symptoms of lice infestation include itching and small, red bumps on the scalp, shoulders and/or neck. Scabies is characterized with itchiness and thin, irregular mite burrow tracks that appear like tiny blisters or bumps on the skin. Dermatitis is evidenced with an itchy rash on swollen, reddened skin. Acne vulgaris appears as blackheads and/or whiteheads, papules, pustules, nodules, and/or cysts.
69. You have just learned that another nurse was fired for taking photographs of patients without their permission using a cell phone and posting them on Face book. This nurse was fired because the nurse has:
- Violated the law
- Acted in a negligent manner
- Not completed the proper documentation
- Violated an ethical principle
Correct Response: A
This nurse was fired because the nurse has violated a federal law, namely, the U.S. government’s Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). This law protects the patients’ rights to the privacy and confidentiality of all medical information, including written, oral electronic information, and personal identity information like photograph taking unless the client has expressly consented to it in writing. Negligence is failing to do something in the proper manner; this invasion of patient privacy is far more serious than a breach of an ethical principle. Lastly, photographs and Facebook posting should never be done so proper documentation is not required. It is still illegal documented or not.
70. Which of the following differentiates ulcerative colitis from Crohn’s disease?
- Crohn’s disease primarily affects the left colon and rectum and ulcerative colitis most often affects the right colon and distal ileum.
- Crohn’s disease presents with shallow ulcerations and ulcerative colitis presents with a cobblestone appearance of the mucosal lining.
- The extent of involvement is noncontiguous and segmented with Crohn’s disease and it is contiguous and diffuse with ulcerative colitis.
- Crohn’s disease has primarily mucosal involvement and it is transmural with ulcerative colitis.
Correct Response: C
The extent of involvement is noncontiguous and segmented with Crohn’s disease; and it is contiguous and diffuse with ulcerative colitis. Other differentiating characteristics include:
The typical area of intestinal involvement is the left colon and rectum for ulcerative colitis and the right colon and distal ileum with Crohn’s disease.
The mucosal appearance has a cobblestone appearance with granulomas with Crohn’s disease; and it appears edematous with shallow ulcerations and superficial bleeding.
The inflammation associated with Crohn’s disease is transmural, and it is mostly mucosal among those with ulcerative colitis.
71. Which atrioventricular heart block is also referred to as Mobitz II?
- Third-degree atrioventricular heart block
- Second-degree atrioventricular heart block
- First-degree atrioventricular heart block
- Complete heart block
Correct Response: A
Third-degree atrioventricular heart block is also referred to as Mobitz II; this type of heart block occurs when the AV node impulses are blocked as they try to reach the ventricles. First degree heart block occurs when the AV node impulse is delayed. Second degree heart block, as referred to as Mobitz I and Wenckebach, occurs when there are progressive conduction delays through the AV node that alters the PR and QRS intervals. Complete heart block blocks all atrial impulses to the ventricle.
72. Which preventive measure can be employed to decrease the risk of compartment syndrome?
- The administration of a potassium sparing diuretic for heart failure
- A bivalve cast for a skeletal fracture
- A cerebral diuretic to decease intracranial pressure after a head injury
- A chest tube to restore normal intrathoracic pressure after a pneumothorax
Correct Response: B
A bivalve cast, rather than a solid fiberglass or plaster of Paris cast, for a skeletal fracture can prevent limb threatening compartment syndrome. Compartment syndrome results from increased pressure and circulatory constriction because a solid cast does not accommodate post fracture swelling like a bivalve cast does. Compartment syndrome is not related to heart failure, head injuries or pneumothoraxes.
73. Which patient is at greatest risk for papilledema?
- An elderly patient with cataracts and macular degeneration
- A male patient with hypothyroidism
- A male patient with hyperthyroidism
- An adolescent with a closed head injury
Correct Response: D
Patients, including adolescents, with a closed head injury is at greatest risk for papilledema because closed head injuries lead to an increase in intracranial pressure which leads to papilledema. Hyperthyroidism is associated with exophthalmos and there is no relationship or positive correlation of macular degeneration and/or cataracts to papilledema.
74. Your patient has been diagnosed with orchititis. What information about this disorder should you inform the patient about?
- This disorder often occurs as the result of a streptococcus.
- This disorder can be symptomatically treated with ice.
- This disorder can be symptomatically treated with heat.
- This disorder is typically treated with surgery.
Correct Response: B
The pain associated with orchiditis, an inflammation of the testicles, is symptomatically treated with the application of ice, not heat, to the groin area. It is not treated with surgery. This infection most often occurs as the result of mumps, the paramyxovirus and some sexually transmitted diseases, not streptococcus.
75. Which of the following healthcare providers can legally have access to all, or part, of a patient’s medical record because they have a “need to know”? Select all that apply.
- Student nurses caring for a particular patient
- Registered nurses when they are not caring for a particular patient
- The Vice President for Nursing who is investigating a patient fall
- Licensed practical nurses caring for a particular patient
- A quality assurance nurse collecting data for a performance improvement activity
Correct Response: A,C,D,E
Medical records are restricted to only those who have a “need to know”. Student nurses caring for a particular patient have the “need to know” so they can properly care for their patient assignment. The Vice President for Nursing, as an administrator, who is investigating a patient fall also has a “need to know” because they are collecting data and information to prevent future falls. Licensed practical nurses caring for a particular patient have the “need to know” so they can provide care to the patient; and the quality assurance nurse has the “need to know” because they are collecting data for a performance improvement activity. No nurse, including registered nurses, are allowed access to all or part of a patient’s medical record unless they have a “need to know” because they are providing either direct or indirect care to the patient.
76. Which cardiac arrhythmia can be either acquired or congenital and can spontaneously disappear on its own or lead to ventricular fibrillation?
- Wenckebach
- Premature arterial contractions
- Torsades de pointes
- Premature ventricular contractions
Correct Response: C
Torsades de pointes, a polymorphic ventricular tachycardia, can be either congenital or acquired; at times, it can spontaneously terminate but it frequently leads to ventricular fibrillation. In some cases cardiac death can occur with the first episode. All of the other cardiac arrhythmias, or dysrhythmias, are acquired and not congenital.
77. Which quality assurance or performance improvement technique is used to identify underlying process flaws?
- Small group process
- Root cause analysis
- People at fault process
- Cause and effect
Correct Response: B
Root cause analysis is a quality assurance or performance improvement technique that is used to identify the underlying, root causes of a problem. Root cause analysis focuses on process flaws and NOT on people who have erred or made a mistake. A cause and effect diagram may be used for root cause analysis but it, in itself, is not a quality assurance or performance improvement technique. Although small groups participate in quality assurance or performance improvement activities, small groups are not a quality assurance or performance improvement technique.
78. Which legal document will most likely contain the patient’s decision to not get cardiopulmonary resuscitation?
- Healthcare surrogacy
- Healthcare proxy
- Advance directives
- Durable power of attorney
Correct Response: C
Advance medical care directives, also referred to as living wills, contain the wishes of the client in terms of treatments and interventions that they do and do not want carried out when they are no longer able to competently provide these consents and rejections of treatment. These legal documents typically include choices relating to cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), mechanical ventilation, intravenous solution administration, life support measures and tube feedings.
A durable power of attorney for health care, also referred to as a healthcare surrogate or healthcare proxy, is a legally appointed person who will make decisions relating to healthcare when the client is no longer competent and able to give legal, informed consent.
79. Select the stage of a pressure ulcer that is accurately pair with its characteristics.
- Stage I: Only slight blanching when pressure is applied to the skin.
- Stage II: The epidermis and part of the dermis is damaged or lost.
- Stage III: The wound has slough and eschar.
- Stage IV: The loss of skin usually exposes some fat.
Correct Response: B
A Stage II pressure ulcer damages the epidermis and part of the dermis. A Stage I pressure ulcer remains intact and the skin doesn't briefly lighten or blanch when touched. A Stage III pressure ulcer is a deep wound that can expose some fat; and a Stage IV pressure ulcer exposes bone, muscle and tendons. It is also characterized with slough and eschar.
80. You have been assigned to care for a neonate who has been diagnosed with the Tetralogy of Fallot. The mother asks you what the Tetralogy of Fallot is. How should you respond to this mother?
- “The Tetralogy of Fallot is a congenital gastrointestinal disorder”
- “The Tetralogy of Fallot is a congenital cardiac disorder”
- “The Tetralogy of Fallot will affect the baby’s reflexes”
- “The Tetralogy of Fallot will affect the baby’s ability to breastfeed”
Correct Response: B
The Tetralogy of Fallot is a congenital cardiac disorder that is classified as a cyanotic, rather than acyanotic, congenital heart disorder that is characterized with abnormal cardiac anomalies. There is no relationship between the Tetralogy of Fallot and reflexes or breastfeeding.
81. The protrusion of an internal organ through a wound or surgical incision is referred to as:
- Serosanguineous.
- Dehiscence.
- Evisceration.
- Exuded.
Correct Response: C
Evisceration, or the protrusion of an organ through a wound, most often occurs in the abdominal wall. Serosanguineous describes the thin, red exudate produced by a surgical wound and dehiscence is the separation of a surgical incision. Exuded is another name for discharged in reference to the exudate.
82. Which pain assessment scale is used exclusively for infants and neonates from 32 weeks of gestation to six months of age?
- The PEPPS pain scale
- The FLACC pain scale
- The Faces pain scale
- The CRIES pain scale
Correct Response: D
The CRIES Pain scale is used exclusively for infants and neonates from 32 weeks of gestation to six months of age. This scale has five behavioral measurements that are scored from 0 to 2; the behavioral measurements include the infant’s crying, requirements for increased oxygen, increased vital signs, expression, and sleepiness. The PEPPS pain scale (Pre-Verbal, Early Verbal Pediatric Pain Scale is used to assess and measure pain among toddlers. The Face, Legs, Activity, Crying, Consolability Scale (FLACC) is used for infants over two months of age and children up to three years of age. The Faces Pain Scale contains cartoon like pictures of six faces ranging from 0, or “no hurt” to 10 which represents “the worst hurt”. It is used for pediatric patients who are three years of age and older.
83. Which of the following is a hazard of immobility?
- Loss of bone calcium
- Increased vital capacity
- Venous vasoconstriction
- A positive nitrogen balance
Correct Response: A
One of the hazards of immobility is the loss of calcium from the bones that results from non weight bearing by the immobilized patient. Other complications, or hazards, of immobility include muscle weakness, muscular atrophy, contractures, disuse osteoporosis, hypostatic pneumonia, pooled respiratory secretions, atelectasis, decreased respiratory movement, decreased, not increased, vital capacity, shallow respirations, diminished cardiac reserve, orthostatic hypotension, venous stasis, venous vasodilation, not vasoconstriction, emboli, dependent edema, stiff and painful joints, thrombophlebitis, urinary stasis, renal stones, urinary retention, urinary incontinence, urinary tract infections, pressure ulcers, diminished metabolic rate, a negative, not positive, nitrogen balance, a negative calcium balance, constipation and depression.
84. How many daily feedings are considered normal for a newborn:
- 8 to 10
- 10 to 12
- 6 to 8
- 12 to 14
Correct Response: B
An average newborn’s stomach empties every 1.5 hours, so common feeding times occur about every 2 hours during a 24 hour period; therefore, 10 to 12 feedings per day is typical. Frequent breastfeeds increase a mother’s prolactin levels, and high prolactin levels are required to establish an adequate milk supply. A higher-frequency of feedings help babies compensate for the lower caloric density of the milk.
85. The hormone produces mother’s milk is:
- Progesterone
- Estrogen.
- Prolactin.
- Colostrum.
Correct Response: C
Prolactin is a protein that is best known for its role in enabling females to produce milk, but it also has other functions, such as regulating the immune system. Progesterone has many roles relating to the development of the fetus during pregnancy. Estrogens are best known for their importance in both menstrual and estrous reproductive cycles. Colostrum is the most nutrient dense part of breast milk produced during the postpartum stage.
86. Which of the following is a life threatening acute complication of diabetes mellitus?
- Neuropathy
- Hypoglycemia
- Retinopathy
- Impaired microcirculation
Correct Response: B
Hypoglycemia is an acute complication of diabetes which can be life threatening. The immediate treatment with glucose is necessary to preserve life. Retinopathy, neuropathy and impaired microcirculation are examples of the long term, rather than acute, complications of diabetes.
87. Sutures and staples are typically removed following surgery within:
- 7 to 10 days if healing is considered adequate.
- 10 to 14 days if healing is considered adequate.
- 7 to 10 days if no further dressings are needed.
- 10 to 14 days if no further dressings are needed.
Correct Response: A
Sutures and staples can be removed within 7 to 10 days if healing has been sufficient and while this removal tends to reduce the amount of dressing supplies needed after removal, a light dressing may still be necessary.
88. Which of these breath sounds is considered normal and not adventitious?
- Vesicular breath sounds
- Fine rales
- Rhonchi
- Wheezes
Correct Response: A
Vesicular breath sounds are normal breath sounds. Rales, fine and coarse, rhonchi and wheezes are all abnormal, adventitious breath sounds.
89. Which type of burn leads to the greatest degree of pain?
- A first degree burn
- A second degree burn
- A third degree burn
- A fourth degree burn
Correct Response: B
Although the first degree burn can cause pain, it is the second degree burn that is the most painful of all. There is a lack of pain with third and fourth degree burns because these burns have destroyed pain sensory nerves.
90. Babies should double their birth weight by the:
- 5th to 6th month.
- 3rd to 4th month.
- 4th to 5th month.
- 5th to 7th month.
Correct Response: C
Most babies should have doubled their birth weight by 6 months, but many may have doubled their birth weight by 5 months of age. Newborns gain about five to seven ounces per week for the first 3 to 4 months of life. By their first birthday, many babies have tripled their birth weight.
91. Which of the following is best for a client who has difficulty swallowing and chokes frequently?
- A liquid diet.
- Tilting the head back when swallowing.
- Tucking the chin in when swallowing.
- Following each bite with a drink of water.
Correct Response: C
The client should tuck the chin when swallowing rather than tilting the head back. Thin fluids and liquids, like water, are thickened prior to drinking to prevent chocking. Tilting the head back is dangerous.
92. How long can women lactate for?
- Indefinitely
- 12 to 18 months
- 18 to 24 months
- 30 to 36 months
Correct Response: A
A woman can lactate indefinitely; however, it puts them at risk of developing osteoporosis due to the calcium depletion from the bones and teeth. Letting the baby wean itself is ideal. Ideally, all babies should be exclusively breastfed for six months with the gradual introduction of solid foods while continuing to breastfeed. Most women in the United States stop breastfeeding following the twelfth month of life.
93. Which anatomic malformations are associated with the Tetralogy of Fallot?
- A sub-aortic septal defect, an overriding aorta, left ventricular hypertrophy, and right ventricular outflow
- A sub-aortic septal defect, an overriding aorta, right ventricular hypertrophy, and left ventricular outflow
- A sub-aortic septal defect, an overriding aorta, pulmonary atresia, and right ventricular outflow
- A sub-aortic septal defect, an overriding aorta, right ventricular hypertrophy, and right ventricular outflow
Correct Response: D
The Tetralogy of Fallot consists of a sub-aortic septal defect, an overriding aorta, right, not left, ventricular hypertrophy, and right, not left, ventricular outflow. Pulmonary atresia is not one of the anatomical malformations included in the Tetralogy of Fallot.
94. Your 32 year old female patient has erythema marginatum, Sydenham chorea, epistaxis, abdominal pain, fever, cardiac problems and skin nodules. What disorder would you most likely suspect based on these signs and symptoms?
- Leukemia
- Histoplasmosis
- Pneumocystis jirovec
- Rheumatoid arthritis
Correct Response: D
Erythema marginatum, Sydenham chorea, epistaxis, abdominal pain, fever, cardiac problems and skin nodules are the signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis. Some of the signs and symptoms of leukemia are fever, bleeding and bruising, shortness of breath, loss of appetite, pain in the bones or stomach and painless lumps in the neck, groin and/or underarm. Histoplasmosis, a fungal infection, is characterized with fever, chills, cough, chest pain, joint pain, mouth sores and erythema modosum. Lastly, the signs and symptoms of Pneumocystis jirovec, among others, can include fever, shortness of breath, rapid breathing and a dry cough.
95. Select the cranial nerve that is accurately paired with its name.
- The first cranial nerve: The trochlear nerve
- The twelfth cranial nerve: The hypoglossal nerve
- The tenth cranial nerve: The olfactory nerve
- The thirteenth cranial nerve: The auditory nerve
Correct Response: B
The twelfth cranial nerve is the hypoglossal nerve. This nerve controls and provides motor innervation to the tongue muscles. The other 11 of the 12 cranial nerves and their functions are listed below:
- Olfactory Nerve: Transmits the sense of smell
- Optic Nerve: Transmits visual signals from the retina of the eye to the brain
- Oculomotor Nerve: Controls most eye movements
- Trochlear Nerve: Moves the eyeballs
- Trigeminal Nerve: Innervates the chewing muscles
- Abducens Nerve: Eye abduction
- Facial Nerve: Controls facial expressions, the lacrimal glands, the salivary glands and other muscles.
- Acoustic Nerve: Gravity, sound and rotation sensations
- Glossopharyngeal Nerve: Senses taste
- Vagus Nerve: It innervates the laryngeal and pharyngeal muscles and controls voice resonance and swallowing.
- Spinal Accessory Nerve: It innervates the trapezius and sternocleidomastoid muscles
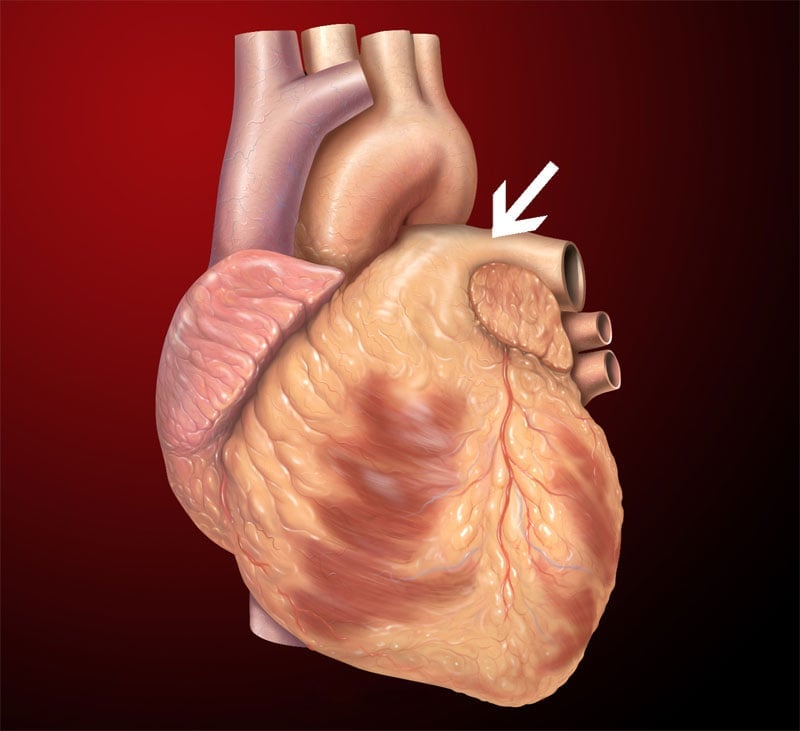
96. What is the name of the section marked:
- Left ventricle
- Right ventricle
- Left atrium
- Right atrium
- Coronary artery
- Pulmonary artery
Correct Response: F
Pulmonary artery
97. Round off these numbers to the nearest hundredth. Fill in the blanks.
- 5.5778 = _________
- 1.027 = _________
- 62.999 = _________
- 55.123 = _________
- 96.679 = _________
Correct Response:
A: 5.58
B: 1.03
C: 63
D: 55.12
E: 96.68
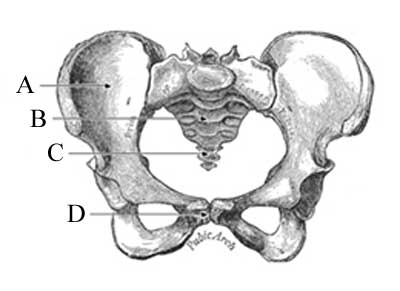
98. Label the following bones of the pelvis:
Correct Response:
A: Pelvis
B: Sacrum
C: Coccyx
D: Symphysis Pubis
99. Round off these numbers to the nearest tenth:
- 5.5778 = _________
- 1.027 = _________
- 62.999 = _________
- 55.123 = _________
- 96.676 = _________
Correct Response:
A: 5.6
B: 1
C: 63
D: 55.1
E: 96.7
100. The doctor has ordered 500 mg of a medication po once a day. The tablets on hand are labeled as 1 tablet = 250 mg. How many tablets will you administer to your patient?
- 1 Tablet
- 2 Tablets
- 3 Tablets
- 4 Tablets
Correct Response: B
This problem is set up and calculated as shown below.
500 mg: X tablets = 250 mg: 1 tablet
Or as 500mg / X = 250mg / 1 tablet
Then you criss cross multiply: 500 mg x 1 = 500 mg
250X = 500 mg
X =500 ÷ 250 = 2 tablets
101. Which patient is exercising their right to autonomy in the context of patient rights?
- An 86 year old female who remains independent in terms of the activities of daily living.
- An unemancipated 16 year old who chooses to not have an intravenous line.
- A 32 year old who does not need the help of the nurse to bathe and groom themselves.
- A 99 year old who wants CPR despite the fact that the nurse and doctor do not think that it would be successful.
Correct Response: D
|
The 99 year old who wants CPR despite the fact that the nurse and doctor do not think that it would be successful is exercising their right to autonomy. Autonomy means that all competent clients have the right to make their own decisions without any coercion or interference even if any or all of their healthcare providers do not agree with this decision. Autonomy is self determination and, in the context of the activities of daily living, autonomy is not related to independence, but only independence in terms of decision making. Lastly, informed legal consents and refusals for treatments, like an intravenous line, is reserved only for those who are not minors and minors who have been emancipated.
|
||
102. The mnemonic “PERLA” is useful for the assessment of the eyes. What does PERLA stand for?
- Pupils equally reactive to light and accommodation
- Patient eyes are equally recessed and responsive to light and acuity
- Patient eyes are equally responsive to light and acuity
- Pupils equally reactive to light and acuity
Correct Response: A
The mnemonic “PERLA” stands for pupils equally reactive to light and accommodation, not acuity. Visual acuity is tested with the Snellen Chart among adult patients.
103. You are performing a neurological assessment of your adolescent patient. The patient has the Moro reflex. How should you interpret this neurological assessment finding?
- It is normal among adolescents.
- It indicates that the patient has an intact peripheral nervous system.
- It indicates that the patient has an intact central nervous system.
- It is not a normal finding.
Correct Response: D
The Moro reflex is a primitive, childhood reflex that disappears long before adolescence and at about 3 months after birth. The Moro reflex is also referred to as the startle reflex. Other primitive, infant reflexes are the sucking, rooting, step, tonic neck, Galant, grasp and parachute reflexes.
104. Which patient is most at risk for Osgood-Schlatter disease?
- An elderly female who is hospitalized with a hip fracture and on bedrest
- A middle aged male patient who has been exposed to asbestos in the shipping industry
- An adolescent who is physically active and the captain of their soccer team
- An infant of low birth weight and a gestational age of 28 weeks
Correct Response: C
An adolescent who is physically active and the captain of their soccer team is at greatest risk for Osgood-Schlatter disease which results from the overuse of the knee and is characterized with patellar tendon inflammation. Other sports that can lead to this disease include running, basketball and gymnastics. Mesothelioma results from asbestos exposure. Lastly, immobility, low birth weight and low gestational age are not associated with Osgood-Schlatter disease.
105. Your client is adversely affected with fever, night sweats, occult hematuria, tenderness of the spleen and Osler’s nodes. What disorder would you most likely suspect?
- Tuberculosis
- AIDS/HIV
- Pericarditis
- Endocarditis
Correct Response: D
The signs and symptoms of endocarditis are fever, night sweats, occult hematuria, gross hematuria, tenderness of the spleen, fatigue, edema and Osler’s nodes which are tender, red spots that can be seen under the skin of the fingers.
106. Your pediatric weighs 15.8 kg. How many pounds does this child weigh?
- 36 pounds
- 33.6 pounds
- 35 pounds
- 34.8 pounds
Correct Response: D
Since there are 2.2 pound in one kilogram, you calculate the weight in pounds by multiplying 2.2 by the kg weight as below.
15.8 kg x 2.2 = 34.8 pounds
107. An episiotomy is:
- A surgical incision of the perineum to prevent tearing during delivery.
- Releasing the red plug from the cervix just before crowning occurs.
- An incision in the abdomen with which the baby can be delivered through.
- The severance of the umbilical cord between mother and child.
Correct Response: A
An episiotomy is a surgical incision of the perineum and the posterior vaginal wall to quickly enlarge the opening for the baby to pass through; this incision prevents tearing during a vaginal delivery. The releasing of the red plug is known as the bloody show. The baby delivered through an incision in the abdomen is a Caesarian delivery. Umbilical severance or cutting and clamping of the cord both apply to the procedure of separating mother and child after childbirth.
108. How many calories per kilogram does an average full term infant require when the infants is around 1-2 months old?
- 140 calories per kilogram per day
- 120 calories per kilogram per day
- 100 calories per kilogram per day
- 160 calories per kilogram per day
Correct Response: B
An average full-term newborn requires 120 calories per kilogram of weight each day to grow into a healthy child. For example, if a newborn weighs 4.55 kilograms, multiply 4.55 by 120. 546 calories would be what an infant should consume in one day.
109. What are the six levels of consciousness from the most to the least responsive level of consciousness. Number all six using 1 as the most conscious and 6 as the least conscious.
- Obtunded
- Confused
- Lethargic
- Comatose
- Stuporous
- Alert
Correct Response:
A: 4
B: 2
C: 3
D: 6
E: 5
F: 1
From the most to the least state of consciousness are alert, confused, lethargic, obtunded, stuporous and comatose.
110. Select the stage of shock that is accurately paired with its characteristic.
- The initial stage of shock: Hyperventilation occurs and the blood pH rises.
- The compensatory stage of shock: Hypoxia occurs and lactic acid rises.
- The progressive stage of shock: Histamine is released; fluid and proteins leak into surrounding tissues and the blood thickens.
- The refractory stage of shock: Potassium ions leak out, sodium ions build up and metabolic acidosis increases.
Correct Response: C
During the progressive stage of shock, histamine is released, fluid and proteins leak into surrounding tissues and the blood thickens. The initial stage of shock is marked with hypoxia and an increase in lactic acid; the compensatory stage of shock is characterized with hyperventilation and rises in the blood pH. The progressive stage of shock is also characterized with the leakage of potassium ions, the buildup of sodium ions and increasingly more severe metabolic acidosis. The refractory, or final, stage of shock becomes irreversible.
111. The doctor has ordered 1,000 cc of intravenous fluid every 8 hours. You will be using intravenous tubing that delivers 20 cc/drop. At what rate will you adjust the intravenous fluid flow? _____ gtts per minute.
- 38 gtts/min
- 42 gtts/min
- 50 gtts/min
- 40 gtts/min
Correct Response: B
42 gtts/min
This calculation is performed using several steps as below.
1000 cc = 125 cc/hr
8
125 x 20 = 125 = 41.6 or 42 gtts rounded off
60 3
112. During which stage of anesthesia is a patient most likely to experience involuntary motor activity?
- Stage I
- Stage II
- Stage III
- Stage VI
Correct Response: B
Stage II, commonly referred to as the excitement stage, is the stage of anesthesia when the patient is most likely to experience involuntary motor activity period; at this time, auditory and physical stimuli must be avoided to reduce the risk of increased tachycardia during this stage. Stage I is the administration phase, Stage III is the surgical phase, and Stage IV is the cessation phase.
113. Select all of the risk factors that are associated with deep vein thrombosis.
- The use of oral contraceptives
- Type B and O blood
- Rh negative blood
- Obesity
- Nulliparity
- Leukemia
Correct Response: A,D
The risk factors associated with deep vein thrombosis are oral contraceptive use, obesity, hormone replacement therapy, hypercoagulable states, old age, type A blood, multiparity, not nulliparity, and among clients who have had major surgery and/or prolonged immobility. Types B and O blood, Rh-negative blood and leukemia are not risk factors associated with deep vein thrombosis.
114. Most water leaves the body by way of the:
- Lungs.
- Intestines.
- Skin.
- Kidneys.
Correct Response: D
The kidneys, via urine, excrete approximately 60% of all water. Water, in lesser volumes, also leaves the body by way of lung expiration, skin perspiration, and through the intestines.
115. Which statement about glaucoma is true and accurate?
- Acute angle-closure glaucoma is an ocular emergency.
- Acute angle-closure glaucoma leads to the loss of peripheral vision and tunnel vision.
- Primary open-angle glaucoma leads to eye pain, nausea and vomiting, blurry vision and halos.
- Bubbles are implanted to protect the retina from the glaucoma.
Correct Response: A
Acute angle-closure glaucoma is an ocular emergency and it is characterized with eye pain, nausea and vomiting, blurry vision and halos. The signs and symptoms of primary open-angle glaucoma are the loss of peripheral vision and tunnel vision. Bubbles are placed to treat retinal detachments, another ocular emergency and laser peripheral iridotomy to decrease intraocular pressure is used for the treatment of glaucoma.
116. A cavity containing pus surrounded by inflamed tissue is:
- Cellulitis.
- An abscess.
- Extravasation.
- An adhesion.
Correct Response: B
A cavity containing pus surrounded by inflamed tissue is an abscess. An abscess is typically formed as a result of suppuration in a localized infection. Cellulitis is an infection of the skin characterized by heat, pain, erythema, and edema. Extravasation is the passage, or escape of blood, serum, or lymph fluids into the tissues. A band of scar tissue that binds together two surfaces that are typically separated is an adhesion.
117. The doctor has ordered 20 cc an hour of normal saline intravenously for your pediatric patient. You will be using a pediatric intravenous tubing that delivers 60 cc per drop. How many drops per minute will you administer using this pediatric intravenous set? Fill in the blank. ____ drops per minute.
- 30 drops per minute
- 25 drops per minute
- 20 drops per minute
- 22 drops per minute
Correct Response: C
You would adjust the intravenous fluid rate to deliver 20 drops of the normal saline every minute. This calculation is performed as below.
20 cc/hr = 60 cc per drop = 20 x 1 = 20 drops per minute
118. What does the mnemonic device ABCDE stand for?
- Allergy, bleeding, chemicals, dietary, environment
- Allergy, bleeding, cardio, diabetes, endocrine
- Allergy, bleeding, cardio, digestive, endocrine
- Allergy, bleeding, cortisone, diabetes, emboli
Correct Response: D
Allergy, bleeding, cortisone, diabetes, and emboli (ABCDE) is a mnemonic that is often used to readily remember some of the serious disorders and risks associated with the perioperative. Allergies to medicines or environment, bleeding tendencies, cortisone or steroid use, diabetes mellitus, and previous embolic events are some of these.
Allergies to medicines or environment, bleeding tendencies, cortisone or steroid use, diabetes mellitus, and previous embolic events are some of these.
119. Which of the following assessment tools is used to determine the patients’ level of consciousness?
- The Snellen Scale
- The Norton Scale
- The Morse Scale
- The Glasgow Scale
Correct Response: D
The Glasgow Scale assesses for altered levels of consciousness. The Snellen chart, not scale, is used to assess and measure visual acuity; the Norton Scale assesses patients’ risk for skin breakdown; the Morse Scale assesses patients’ risk for falls.
120. Wilms’ tumor is a form of:
- Renal cancer.
- Liver cancer.
- Basal cell carcinoma.
- Brain cancer.
Correct Response: A
Wilms’ tumor, although rare, is a type of renal cancer. People of all ages can be affected with it, however, it is most common among members of the pediatric population. The treatments for Wilms’ tumor include radiation therapy, chemotherapy and surgical removal.
121. You will be reinforcing teaching and instructing the patient. Which basic principle of teaching should you follow?
- Sequence the instruction from the least complex to the most complex.
- Assume that the patient knows little or nothing about the topic.
- Tell the patient to call their significant other so you can instruct them.
- Use medically oriented terms so the patient will be able to speak with the doctor.
Correct Response: A
You should sequence the instruction from the least complex to the most complex when reinforcing teaching and instructing the patient. For example, if you are instructing the patient about coughing and deep breathing, you should begin the instruction by demonstrating normal breathing, then deep breathing and finally combining deep breathing with coughing. You should not assume that the patient knows little or nothing about the topic, you should determine what they know. It is not necessary to have the patient call their significant other so you can instruct them; this is only necessary when the patient is not able to understand the instructions. Lastly, you should not use medically oriented terms and medical jargon, but instead, terms that the patient understands.
122. As you are administering penicillin intravenously, you determine that the patient becomes hypotensive and with a bounding, rapid pulse rate. What is the first thing that you would do?
- Decrease the rate of the intravenous medication flow.
- Increase the rate of the intravenous medication flow.
- Call the doctor.
- Stop the intravenous flow.
Correct Response: D
This patient is experiencing the signs and symptoms of anaphylactic shock which is a severe life threatening allergic response that is often associated with a penicillin allergy or hypersensitivity. The first thing you should do is stop the intravenous flow and respond to this medical emergency which can lead to death. After this you should call the doctor about this episode and inform the doctor of the patient’s current medical status.
123. Your patient has a blood potassium level of 9.2 mEq/L. What intervention should you anticipate for this patient?
- Intravenous potassium supplementation
- Intravenous calcium supplementation
- Kidney dialysis
- Parenteral nutrition
Correct Response: C
The normal potassium level is 3.7 to 5.2 mEq/L. A patient with a blood potassium level of 9.2 mEq/L is affected with severe hyperkalemia which can be life threatening. Medications, such as Kayexalate, are administered to rid the body of excessive potassium and emergency kidney dialysis may also be done to prevent life threatening cardiac arryhythmia and death. Potassium supplementation is used with hypokalemia and not hyperkalemia; calcium supplementation and parenteral nutrition have no therapeutic effects for the treatment of hyperkalemia.
124. Which of the following foods enhances the absorption of an iron supplement?
- Orange juice
- Green beans
- Fortified Milk
- Baked potato
Correct Response: A
Vitamin C aids in the absorption of iron, and orange juice is a reliable source of Vitamin C. Green beans, milk, or baked potatoes do not support the absorption of iron; they do not contain the necessary vitamin C.
125. Select a myth or falsehood relating to pain, pain management and addiction.
- Addiction can be accurately predicted.
- Withdrawal, drug tolerance and physical dependence do not indicate addiction.
- Pain medications can be used with patients who have a substance abuse history.
- Addiction is signaled when the client employs deception and stockpiling.
Correct Response: B
Withdrawal, drug tolerance and physical dependence do not indicate addiction as many people believe. All the other statements are incorrect and myths relating to pain and pain management medications.
126. What is the expected date of delivery for the woman who has had their last menstrual period on April 20th?
- January 20th
- January 27th
- January 29th
- January 31st
Correct Response: B
According to Nagle’s rule, this estimated date of delivery is calculated as below:
The First Day of the Last Menstrual Period: April 20th
Subtract 3 Months: January 20th
Add 7 Days: January 20th plus 7 days = January 27th
Estimated Date of Delivery: January 27th of the following year
127. Clumsiness, difficulty running, climbing, and riding a bicycle are some of the earliest signs and symptoms of:
- Duchennes’s muscular dystrophy
- Osteomyelitis
- Talipes or clubfoot
- Septic joint, suppurative arthritis
Correct Response: A
Clumsiness, difficulty running, climbing, and riding a bicycle are some of the earliest signs and symptoms of Duchenne’s muscular dystrophy. This disorder is a sex-linked inherited genetic skeletal muscle wasting disorder and it is the most severe and most common of all dystrophies. Osteomyelitis is an infection with the bone. Talipes is a deformity of the foot and ankle and it is physically discernible. Septic arthritis is an infection of a joint that will also show visible signs of its presence.
128. Which statement about adjuvant medications is true and accurate?
- Licensed practical nurses cannot administer adjuvant medications.
- Adjuvant medications are schedule 2 narcotics.
- Adjuvant medications are schedule 1 narcotics.
- Adjuvant medications can be purchased over the counter.
Correct Response: D
Adjuvant medications, used to increase the effects of the opioids and nonopioid medications. These medications include anxiolytics, anesthetics, anticonvulsants, nonsteroidal analgesic medications and topical local anesthetics. Some of these medications, like ibuprophen, are available over the counter and they act on pain by deadening the nerve endings in the skin. Invasive local anesthetics are also used for severe pain, as below.
129. Which nonpharmacological technique entails the use of electronic monitoring equipment while the patient controls basic bodily mechanisms?
- Meditation
- Visualization
- Biofeedback
- Chiropractic
Correct Response: C
Biofeedback is a nonpharmacological technique that entails the use of electronic monitoring equipment while the patient controls basic bodily mechanisms such as body temperature, sweating, heart rate, blood pressure, muscle tension and sweating.
130. Which of the following is considered normal for the neonate?
- Chest Circumference: 10 to 13 inches
- Length: 16 to 22 inches
- Weight: 1,500 to 4,000 g
- Head Circumference: 12.6 to 14.5 inches
Correct Response: D
The normal and expected parameters for the neonate in terms of head circumference is 12.6 to 14.5 inches. The other normal measurements are:
Length: 18 to 22 inches (45 to 55 cm)
Weight: 2,500 to 4,000 g
Chest Circumference: 12 to 13 inches
131. Your patient has been diagnosed with giant cell arteritis. What medication will this patient most likely be given?
- High doses of aspirin
- High doses of prednisone
- Methotrexate
- Albuterol
Correct Response: B
Patients with giant cell arteritis are treated low dose aspirin and high-dose prednisone. Giant cell arteritis is an inflammatory condition that affects medium and large vessels, including the temporal artery and the carotid artery. Methotrexate is used for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, not arteritis; and albuterol is an inhaled medication that is used for the treatment of bronchitis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
132. The wound irrigation process cleanses the wound and:
- Reduces the potential of pain in the wound region or area.
- Stops the spread of infection by way of magnifying the “clean” area.
- Pushes extravasated blood from a hematoma into nearby healthy tissue.
- Allows for the introduction of medications in solution form.
Correct Response: D
Of all the choices above, the only correct fact about wound irrigation is that it allows the application of medications in solution. Introducing prescribed medications in solution form can dramatically reduce infection risks and facilitating proper wound heal. Unfortunately, the irrigation process can greatly increase the pain in a wound area. Wound irrigation can reduce the spread of infection, but not by increasing the area cleaned. The complications resulting by a hematoma are reduced through wound irrigation and not by pushing into other tissue.
133. You are caring for a four year old female patient who was severely burned in a house fire. How would you determine the extent of this child’s burns?
- By using the Lund and Browder chart
- By using the Rule of Nines
- By using the Rule of Tens
- By using the Parkland Formula
Correct Response: A
The Lund & Browder burn chart is used to determine the extent of burns among the members of the pediatric population. Adults are assessed by using the Rule of Nines and not the Rule of Tens. Lastly the Parkland Formula is used to determine the fluid needs of burn patients and not to determine the extent of their burns.
134. Your client has a doctor’s order that reads “advance diet as tolerated”. This client has returned from the recovery room after an appendectomy and he states, “I am hungry”. What would you offer this client to consume?
- Cheese and crackers
- Apple sauce
- Chicken broth
- A peanut butter sandwich
Correct Response: C
Clear liquids are the most appropriate choice for any postoperative patient. If the client tolerates these choices well, the diet may proceed to full liquids. Eventually, solid foods will be added to his diet.
135. Idiopathic thrombocytopenia purpura is:
- Highly similar to disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC).
- Caused by the over production of platelets.
- A bleeding disorder that is characterized with too few platelets.
- Treated with immune system boosting medications.
Correct Response: C
Idiopathic thrombocytopenia purpura is bleeding disorder that is characterized with too few platelets, not the over production of platelets. Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is characterized with blood coagulation and not bleeding. The treatments of idiopathic thrombocytopenia purpura can include immune system depressants, not stimulants, prednisone, high-dose gamma globulin and anti RhD therapy.
136. Select the type of skeletal fracture that is correctly paired with its description.
- A complete fracture: The fractured bone penetrates through the skin to the skin surface.
- A pathological fracture: A fracture that results from some physical trauma.
- A greenstick fracture: This bends but does not fracture the bone.
- An avulsion fracture: A fracture that pulls a part of the bone from the tendon or ligament
Correct Response: D
An avulsion fracture pulls a part of the fractured bone from the ligament or tendon. A complete fracture is one with which the whole cross section of the bone is fractured; a compound or opened fracture pierces through the skin; a pathological fracture results from an underlying disease or disorder not physical trauma or stressors. Lastly, a greenstick fracture is a skeletal bone fracture that affects only one side of the bone.
137. Select the criteria that is accurately paired with its indication of birth weight or gestational age.
- Low birth weight: The neonate’s weight is less than 1,500 g at the time of delivery.
- Appropriate for gestational age: The neonate’s weight ranges from the 10th to the 90th percentile.
- Large for gestational age: The neonate’s weight is above the 99th percentile.
- Small for gestational age: The neonate’s weight is below the 20th percentile.
Correct Response: B
It is considered appropriate for gestational age when the neonate’s weight ranges from the 10th to the 90th percentile. A low birth weight is less than 2,500 g at the time of delivery. Large for gestational age is indicated when the neonate’s weight is above the 90th percentile and when the neonate’s weight is below the 10th percentile, it is considered small for gestational age.
138. Diabetes insipidus is the result of:
- A diet high in sugar and carbohydrates.
- A complicated pregnancy.
- A disorder of the pancreas.
- A disorder of the pituitary gland.
Correct Response: D
Diabetes insipidus is the result of a pituitary gland disorder although it can also occur as the result of a brain infection or tumor as well as a closed head trauma that impacts on the pituitary gland. Diabetes insipidus is a lack of antidiuretic hormone secretion from the pituitary gland and the signs and symptoms include polyuria, polydipsia, hypernatremia and dehydration.
139. Which position will you place your patient in when they are demonstrating the signs and symptoms of hypovolemic shock?
- The Trendelenberg position
- The supine position
- The left lateral position
- The right lateral position
Correct Response: A
You would place your patient in the Trendelenberg position when they are experiencing the signs and symptoms of hypovolemic shock. This position places the legs of the patient higher than the head and it increases the return of the blood in the extremities back into the circulating blood, thus increasing blood volume and the blood pressure, in addition to other necessary emergency measures. The supine, left lateral and right lateral positions do not produce this effect.
140. The fine, down-like hairs on the newborn’s ears, shoulders, lower back, and/or forehead are known as:
- Vernix.
- Lanugo.
- Milia.
- Vibrissea.
Correct Response: B
The fine, soft hair found on a newborn’s body is referred to as lanugo. Vernix is creamy substance that protects the skin, milia are the tiny white bumps found on the nose and cheeks, and vibrissea are the small hairs found in the nasal vestibule of the newborn.
141. What is the softening and thinning of the cervix during labor known as?
- Dilation
- Symphysis
- Effacement
- Hyperplasia
Correct Response: C
Effacement is the softening and thinning of the cervix; dilation is the opening of the cervix. The symphysis is the midline joint connecting the left and right pubic bones. Hyperplasia is the increase of tissue that results from cell proliferation, such as when the milk-secreting glandular cells in the breast experience growth and multiplication as a response to pregnancy.
142. Which of the following joints normally has 360 degree circumflexion?
- The knee
- The shoulder
- The elbow
- The finger tips
Correct Response: B
The shoulder normally has 360 degree circumflexion. It can move in a complete circle. The other joints are capable of flexion and extension.
143. Which healthcare associated infection is the greatest risk for patients?
- Pneumonia
- Catheter related infections
- Intravenous line infections
- C. difficile
Correct Response: B
Catheter related infection is the most commonly occurring healthcare associated infection, therefore, these infections are the greatest risk for patients. For this reason, indwelling urinary catheters are used only when necessary and, then, they remain in place for the briefest period of time possible. Pneumonia, intravenous line catheters and C. difficile are all healthcare associated infections, however, they do not occur as frequently as indwelling urinary catheters do.
144. Select the nursing theorist who is accurately paired with the theory or model of nursing that they are credited with.
- The Twelve Nursing Problems: Faye Glenn Abdellah
- The Nature of Nursing: Imogene King
- The Goal Attainment Theory: Virginia Henderson
- The Interpersonal Relations Model: Hildegard Peplau
Correct Response: D
Hildegard Peplau is credited with the Interpersonal Relations Model; Faye Glenn Abdellah developed the Twenty-One Nursing Problems; Imogene King is credited with the Goal Attainment Theory; and Virginia Henderson is credited with the Nature of Nursing Theory.
145. Which technique or method is used to determine whether or not the patient has an irregular pulse?
- Apical pulse
- Inspection
- Auscultation
- Percussion
Correct Response: C
Auscultation is listening to the sounds of the body, particularly the apical pulse for rate and irregularity, using a stethoscope. Inspection is the purposeful and systematic visual inspection and examination of the client. The palpation technique employs the nurse’s sense of touch. Percussion is performed by striking the client’s body in order to determine what sounds and vibrations their body will produce.
146. Select the tactile sensation that is accurately paired with its description or procedure for testing.
- Fine motor coordination: The use of the fingers
- Stereognosis: Equal hearing in both ears
- Two point discrimination: The nurse gently pricks the patient’s skin
- Gross motor function: The use of the lower limbs
Correct Response: C
In order to determine one and two point discrimination, the nurse gently pricks areas of the skin and the client states whether or not they feel these pricks while their eyes are closed. Both fine and gross motor coordination are not tactile sensations but instead indications of muscular function. Lastly, stereognosis is a tactile sensation and it has no role in hearing. A familiar item like a button, a pen or a paper clip is placed in the person’s hand with their eyes shut. The nurse then asks the person to identify the familiar object.
147. Which is considered an internal disaster?
- A patient fall
- The massive spread of pneumonia
- A computer hacking episode
- Unexpected staff absences due to illness
Correct Response: C
A computer hacking episode is considered an internal disaster. It threatens patient privacy of information and the secure ongoing manner of communication within the healthcare facility. Other internal disasters include utility failures, a power outage, workplace violence and a tornado or other environmental threat. A fall is an incident, accident and sentinel event. The spread of infections, like pneumonia, is an infection control concern but not considered an internal disaster. Unexpected staff absences disrupt the facility but they are not considered internal disaster.
148. Who is credited with the stages of cognitive development?
- Erikson
- Piaget
- Freud
- Lister
Correct Response: B
Jean Piaget is credited with the stages of cognitive development from infancy until the age of twelve. Erikson developed the psychological stages of development and their correlate developmental tasks from infancy to older age; Freud developed the psychological stages of development; and Lister is considered the “Father of Infection Control” and the person who discovered antibiotics.
149. You are working on a pediatric unit. Which toy or other diversional item or activity is most appropriate for your 18 month old patient?
- A story book
- A beach ball
- An interactive play session with other children less than 2 years of age
- Pickup sticks
Correct Response: B
The toy or other diversional item or activity that is most appropriate for your 18 month old patient is a beach ball. This ball is safe for the child. It is too large for the child to put into their mouth and it is not sharp, like pickup sticks are. A story book is not appropriate because the child is not yet able to read and an interactive play session is not appropriate because children of this age do not interact in play, instead, they engage in side by side play, also referred to as parallel play.
150. You are caring for a patient who has no cognitive functioning but only basic human functions such opening the eyes and the sleep – wake cycle. What level of consciousness does this patient have?
- Obtunded
- A persistent vegetative state
- Locked in syndrome
- Brain death
Correct Response: B
A persistent vegetative state leaves the client with no cognitive functioning but only basic functions such as a sleep – wake cycle and eye opening. Locked in syndrome is characterized with retained cognitive functioning but absent motor functioning. This patient is able to communicate with eye movements and they are typically aware of their surroundings. Brain death is defined as the state where there is a known irreversible cause of the coma, a complete loss of all brainstem reflexes, complete unresponsiveness to eternal stimuli and the absence of respiratory function with the presence of hypercapnea. Obtunded patients respond slowly to stimulation.